Researchers continue studies of extracellular vesicles for injury rehabilitation in animals
Co-author, Head of the Laboratory of Gene and Cell Technologies Albert Rizvanov notes, “Spinal cord injuries are among the serious challenges in contemporary healthcare and cause severe disabilities. Existing treatments do not provide full rehabilitation.”
Vesicles are cell structures composed of cell membranes. They contain cytoplasm and a double lipid layer and are involved in various processes in the body, from coagulation to pathology. In a study aimed at developing a new approach to treating spinal cord injuries, extracellular vesicles of the pig were used.
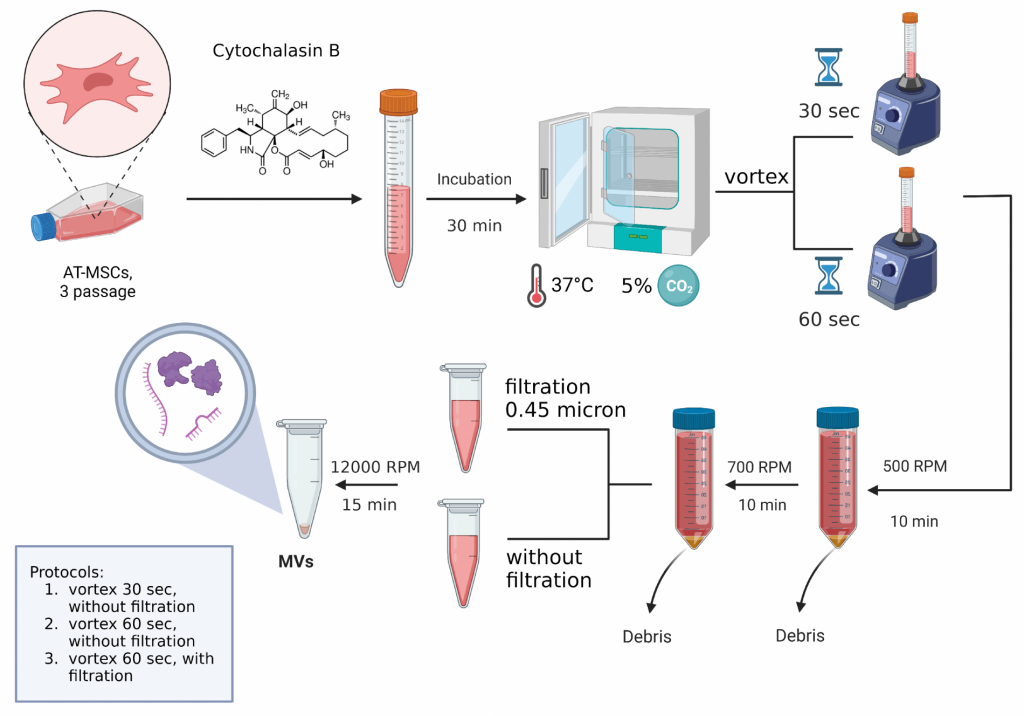
Team leader Yana Mukhamedshina explains, “Extracellular vesicles were obtained from mesenchymal stem cells with cytochalasin B using various protocols of mechanical impact and filtration. A qualitative assessment of these vesicles was carried out, their size and ultrastructure were determined using transmission electron microscopy.”
“In the course of the study, the long-term functional (motor function, conduction along nerve fibers) and structural (safety of tissue in the area of damage, changes in the cellular composition) results of repeated intrathecal injections of autologous extracellular vesicles obtained from mesenchymal stem cells were analyzed in a model of spinal contusion injury. brain in pigs,” adds Mukhamedshina.
The results of the experiments indicate a partial recovery of motor activity in pigs with contusion spinal cord injury due to stimulation of axonal remyelination and timely reperfusion of the nervous tissue.
Pilot trials are conducted at the Republican Clinical Hospital to evaluate the prospects of such therapy in humans.

