Neurosurgeons of the University Clinic perform local injections of anti-inflammatory drugs under X-ray control
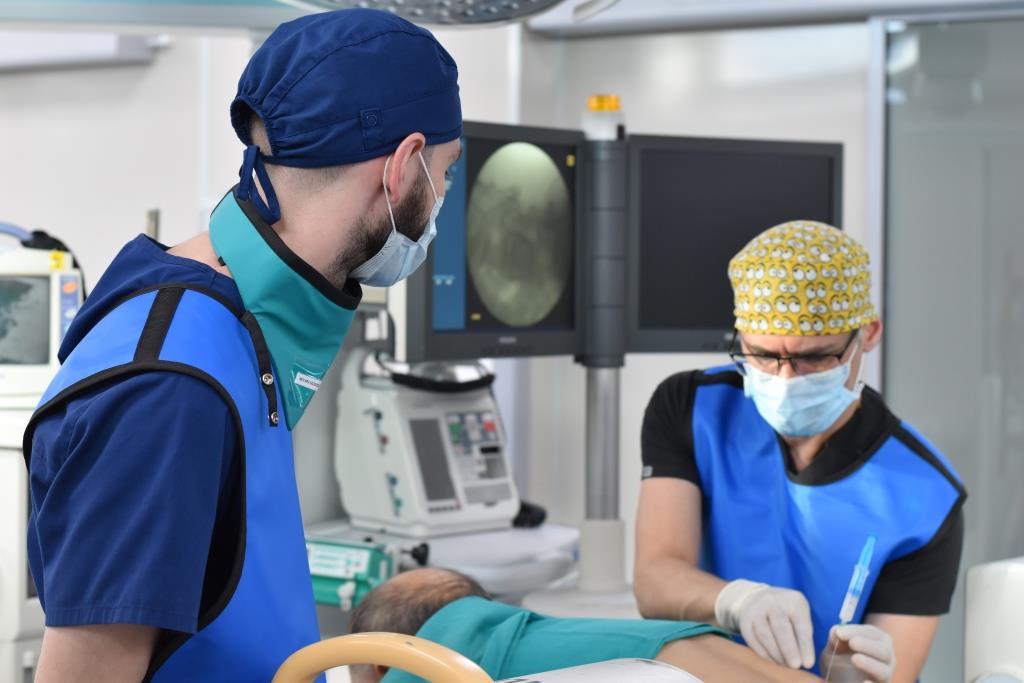
These procedures are many times more effective than classical ‘blind’ local blockades due to high accuracy and safety.
One of the types of these injections is the transforaminal epidural blockade. It is a targeted injection of a drug controlled in real time by an X-ray unit (C-arc) into the perineural and epidural space.
Transforaminal epidural injection is a complex, high-tech procedure using expensive equipment that requires specialized staff training. Neurosurgeons at KFU Clinic perform it according to clinical protocols recognized worldwide.
“During the procedure, a drug mixture consisting of a local anesthetic and a long-acting steroid is injected into the epidural space under C-arc control. Before injecting the anti-inflammatory drug, we apply a special contrast agent to make sure the procedure is safe and accurate. The solution of small volume (only about 3-5 ml) is distributed perineurally, epidurally and gets directly into the zone of compression of nerve structures,” says neurosurgeon Andrei Vershinin.
The action of the drug can be divided into two stages. First, anesthetics block the pain signal from the compressed root. This gives a short-term result. After the end of the action of the anesthetic, pain may return, but its intensity lessens.
At the same time, the action of the anti-inflammatory steroid drug begins. Because the drug is present in a sustained-release form, its effects last for several weeks, and the effects may persist for many months. As a result of the suppression of the inflammatory response, the swelling of the root is reduced, and the degree of compression is significantly decreased, which leads to a rapid reduction in pain.
Indications for local injections under X-ray control include herniated discs, degenerative-dystrophic spine diseases (osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis, disc protrusions), stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal and intervertebral foramen (foraminal stenosis), and spondylolisthesis (vertebral displacement).

